|
|
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
□ Introduction
of A113 Laboratory |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
Our research group working on energy
and advanced technology applications through the investigation of solid oxide
fuel cells, Photocatalysis for Wastewater treatment, Hydrogen Evolution through
water splitting. |
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
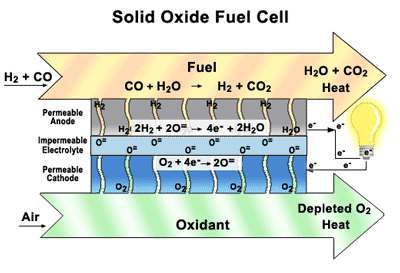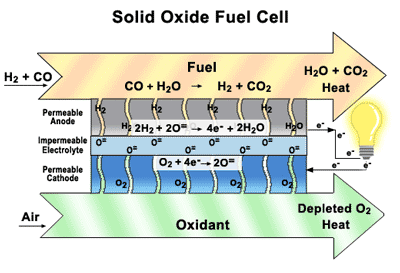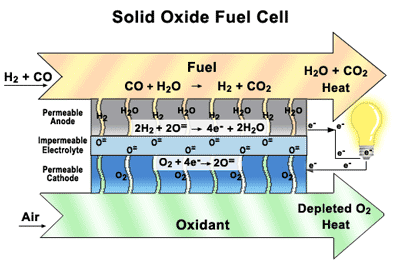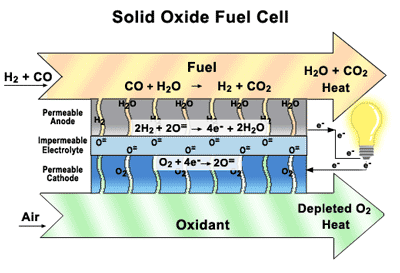
Solid Oxide Fuel Cells (SOFCs) Our research focuses on how materials function in solid
oxide fuel cells (SOFCs)—their durability, damage tolerance, and performance
over time. By designing the component parts and understanding how they interact
with each other. SOFCs are similar to batteries, except they are constantly
replenished with fuel and never run down. They are highly efficient, they don’t
create noise pollution or release toxins into the environment, they can directly utilize a wide variety of commonly-available fuels,
including natural gas, biogas, ethanol, methanol, hydrogen, carbon monoxide,
and synthesis gas produced from coal or natural gas, without the thorough and
extensive purification required for low-temperature fuel cells. SOFCs offer the benefits of sustainable electric power
without the drawbacks of other alternative energy generators. They are a
convenient, portable source of clean energy, unlike solar panels or wind farms,
which depend on fickle natural elements and massive infrastructure. SOFCs are
inexpensive to produce and require no new infrastructure investments. Our main goal of research to find a good layered perovskite materials working in the intermediate temperature and the extensive studies Oxygen permeation, Thermal, Mechanical and Electrochemical properties.
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
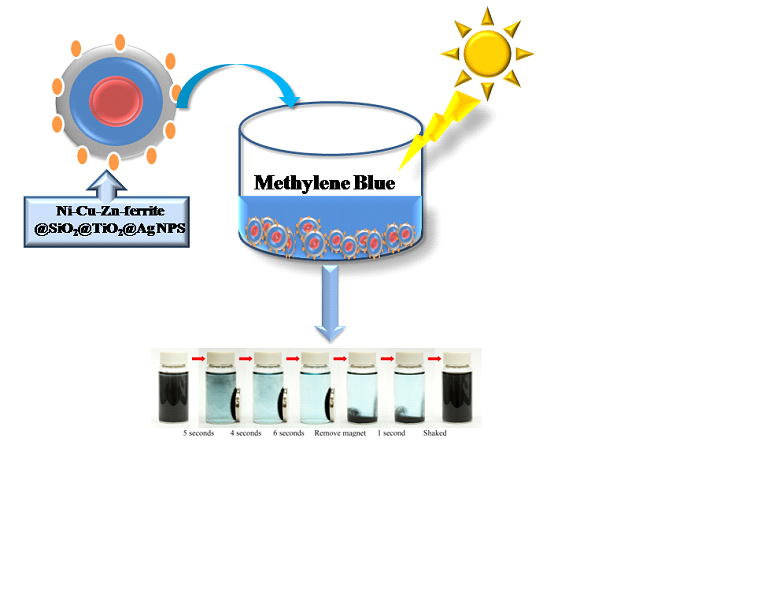
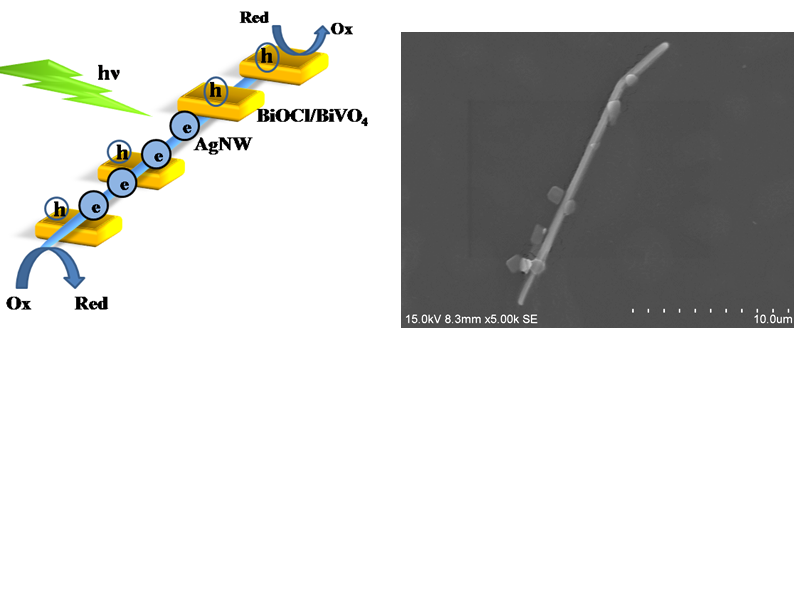
Photocatalysis Photocatalysis for Hydrogen
production and water pollutant treatment are important research area for
addressing global energy needs and environmental issues. Treatment of wastewater containing
persistent organic and inorganic pollutants, prior to disposal into the
environment, has attracted substantial interest over the past decades. The project will
focus on fabrication of low cost, non toxic and highly efficient
photocatalysts and their application in wastewater treatment. The relevant
reaction mechanism will also be investigated by spectroscopies and other
advanced technologies, which will be fed back to the material synthesis to
improve the catalytic efficiency.
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Tthe Material of Resource Recycle Utilizing recoverable
material again that refined out from the pollution by scientific method, it is one of the developing directions in
this laboratory. The pollution
sources may come from: 1.
chemical industry 2.
The
waste of pernicious and noxious They have many kind
of project of this laboratory developing. In general, the traditional methods
of heavy metal waste water treatment including (1) Ion exchange The
micro-pollutant removed after the tradition law processing in the waste
water. Accord the stricter environmental protection regulation, cleaning and
recycling the waste water that is the electroplate solution include trace ions.
That makes the purified water reflow and used usefully again. (2) Evaporation The method is
recycling the chemical medicines form electroplates washing water. That
removes large of water by heat to boil. The recycling medicines are
concentrated then reuse in the electroplate bath. (3) Electrolysis Metal recycles by
deposition from dilute solution, and the law especially applies to the noble
metal. (4) Neutralization Precipitate For the waste
water of much metal ions, those also add the base solution to make it produce
the hydroxide precipitating, which called Neutralization Precipitate.
Sometime addition Fe2(SO4)3, Al(SO4)3
or macromolecule agglutinate, make the heavy metal ions precipitate at lower
pH by congeal precipitation. The method can let waste water to flowing
standard, but the method will produce much heavy metal mud that dehydrates
difficultly. If abandon the dehydrate mud arbitrarily, that will dissolve out
the heavy metal ions to make second environmental pollution by rain and
groundwater. So must give some solidify device to the mud, because the mud is
an unstable hydroxide, and the stable mud that can do oxidation and
reduction. That also make the solidify body to crumble and split easily, that
will pollute the environment again. Our focuses on
improve the various method of pollutant treatment, that can reduce and
improve the disadvantage of traditional treatment method, and develop the new
technology of resource treatment actively. We expect the research results
that can have some contribution for environmental protect in the future. |
|
|||
|
|||||
|
|